What is ASM?
Attack Surface Management (ASM) provides you the ability to see all services exposed to the public internet across your global estate in real time.
As new systems are deployed, decommissioned, or a system changes, ASM can inform you of the event. This is delivered in real time and on a continuous basis.
ASM is about visibility. “We can’t secure what we can’t see.” Its purpose is to Identify security blind spots and map all assets discovered in your global IT ecosystems. It continuously evaluates information in real-time as new assets are deployed, decommissioned or as a system changes.
Edgecan’s ASM also checks for potentially unknown systems which may be relevant to you and are avenues for an attack against your organization. Some edgescan features are:
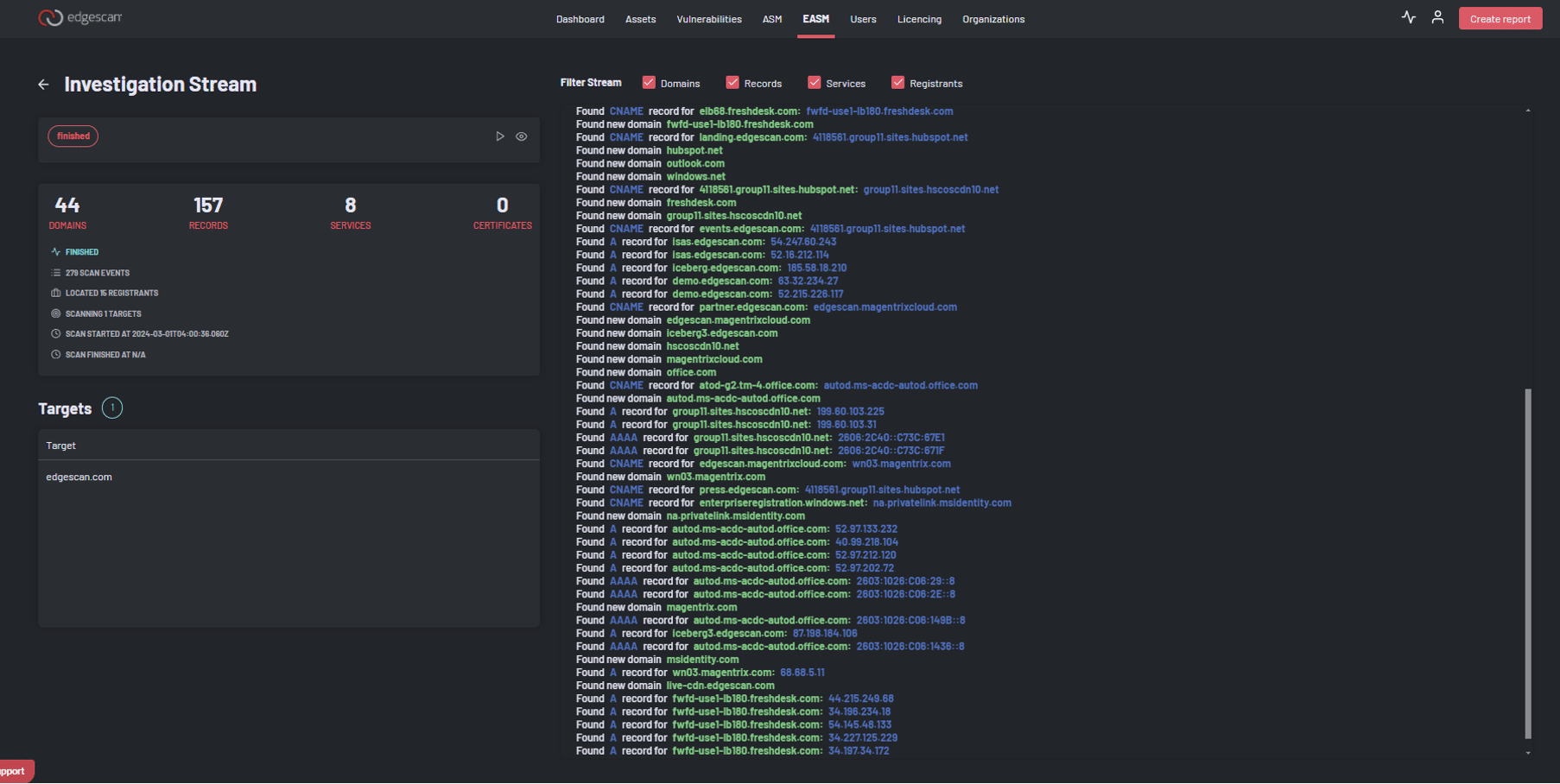
Brute-force subdomain enumeration uses a brute-force approach to guess potential subdomains of target domains. Why?
Reducing Attack Surfaces: Subdomain enumeration helps identify and map the subdomains associated with a domain name. By discovering these subdomains, security professionals can narrow down the scope of an organisation’s landscape. Knowing which machines and resources are available allows for targeted assessments and reduces the preparatory work needed to locate and map the organization’s infrastructure. “Knowing what we have so we can secure our landscape”.
Subdomain Enumeration is also designed to for detecting hidden applications which leads to additional vulnerability discovery.
Last registrant exploration retrieves the last (most recent) registrant of a domain. Why?
Understanding Ownership history. Security and trademark protection to help detect misuse or violation of intellectual property.
Domain DNS resolution resolves the DNS records of a domain. Why?
DNS resolution can assist with load balancing investigations, redundancy and failover and DNSSEC such as malware blocking, content filtering and global accessibility.
Subdomain enumeration discovers subdomains of target domains by querying publicly available resources like search engines and social media. Why?
Subdomain enumeration helps identify all subdomains associated with a domain. Cybersquatters spend time discovering additional targets beyond the main domain.
Each subdomain potentially represents an opportunity for squatting. By enumerating subdomains, cybersquatters can find unknown applications or services that might be vulnerable or valuable for their purposes.
Attackers may monetize or infect squatted subdomains through malware, ads, affiliate marketing, or selling them to the highest bidder. Subdomain enumeration helps them discover potential targets for such activities.
Certificate retrieval and certificate health retrieves certificates for domains and reports their validity and expiration dates. Why?
Assess encryption strength to detect weaknesses in cryptography which may result in breach or vulnerability. Assistance with compliance, given weak certificates can result in compliance fails.
Revoking compromised certificates is important. Healthy certificates demonstrate adherence to security requirements.
Search engines consider HTTPS (secured by TLS) as a ranking factor. Healthy certificates positively impact SEO.
Service Discovery discover exposed ports and running services on discovered domains. Why?
Understand your landscape and discover exposures related to what’s deployed. Not all exposures are vulnerabilities but simply services that should not be exposed (E.g., Remote desktop, FTP, Database exposed etc. – possibly to the service is unknown or firewall is misconfigured).
HTTP Probing probe HTTP(s) service availability and status. Note that this is redundant if you are also using the Service Discovery task. It is offered as a lightweight alternative for situations where port scanning would not be appropriate.
Registered Domains exploration finds domains that are registered or have been registered in the past by the same entity that registered a target domain. Why?
Understanding the history of a domain may help with contact details, understanding SEO, blacklisting, past usage, domain reputation, and domain health.
Typosquatting and similar domain discovery reports domains that are lexicographically similar to target domains. This can help identify typosquatting and domains using other TLDs with the same name. Note that this task can take a long time to complete and may generate a lot of noise.
Why is it important?
ASM is an important tenant in vulnerability detection and management. We need to continuously keep abreast of our landscape to help ensure it is all undergoing a level of vulnerability detection and focus.
Is ASM Penetration Testing or Vulnerability Management?
ASM is all about visibility The term has been twisted and stretched to include vulnerability scanning and Penetration testing but ASM in effect is measuring the landscape (attack surface). Once we understand the landscape we can “push” such intelligence to RBVM (Risk based Vulnerability Management) and tee up for penetration s required.
How Edgescan looks at ASM
Edgescan views ASM as 1. Discovery and mapping of landscape and, 2. Continuous profiling of discovered assets. Once items are discovered they may have some exposures which are not specifically CVE’s or “vulnerabilities” per se, but just services which should not be exposed (such as remote login, administration or database services exposed).
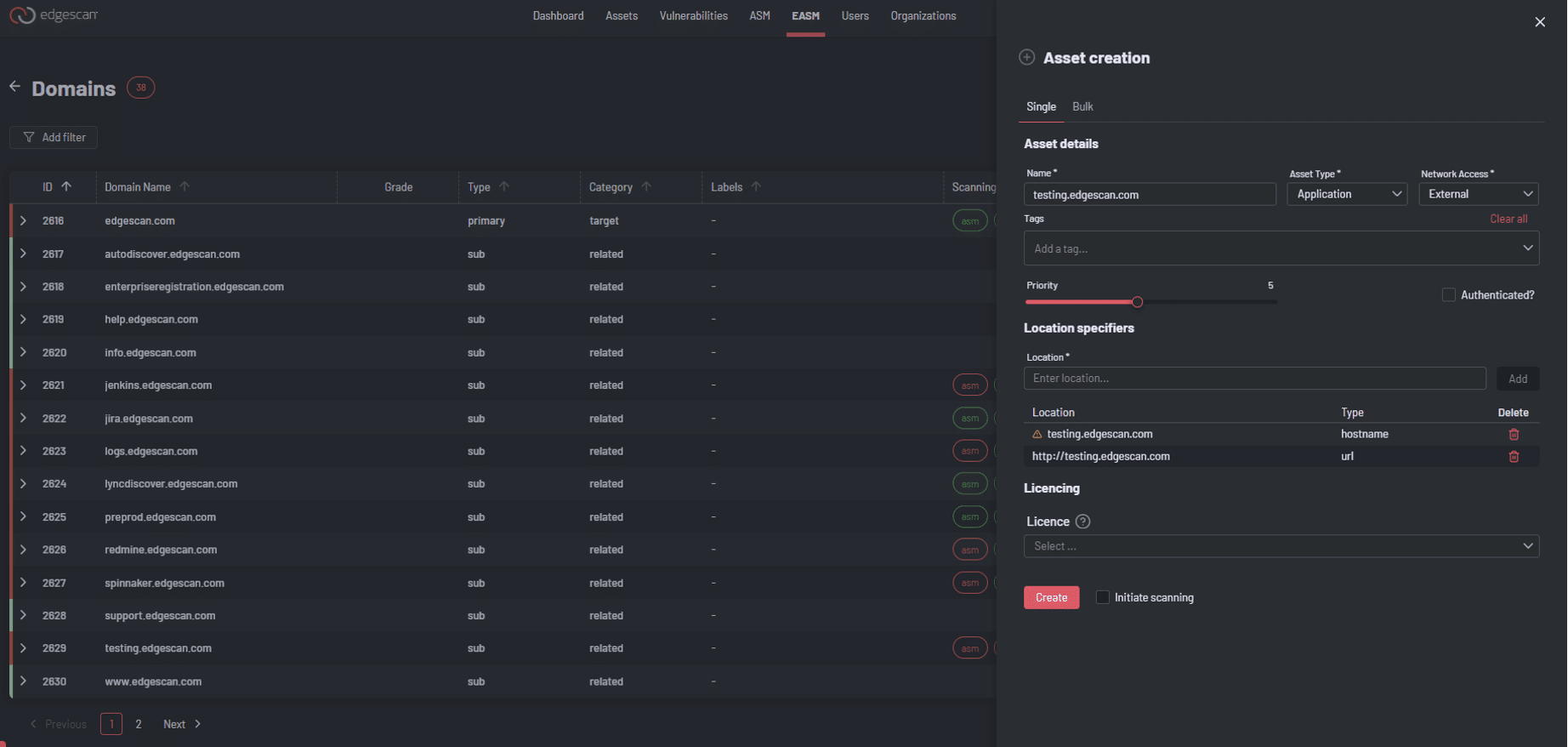
In Edgescan you can add (via one-click) a newly discovered asset to our RBVM or PTaaS functions to undergo validated full stack scanning, API assessment or Web application Penetration as a Service (PTaaS).
Fig 3. Adding a newly discovered asset in EASM to RBVM or PTaaS
Coupling ASM with RBVM & PTaaS
- Discover new assets not under vulnerability management or not undergoing PTaaS and unexpected assets owned by your organization which are a surprise.
- One-click to add the asset to an unlimited RBVM schedule or schedule for penetration testing.
- Continuously monitor asset for services, changes and exposures.
It is as simple as that:
- ASM for visibility and landscape (attack surface) mapping
- RBVM for continuous scanning for Web applications and host/network vulnerabilities (full-stack)
- PTaaS for deep penetration testing using OSCP & CREST certified testers