- THE PLATFORM
- FEATURES
The Edgescan Platform eliminates the need for tool configuration, deployment, and management.
By providing vulnerability intelligence and remediation information along with human guidance and vulnerability verification, we help our customers prevent security breaches, safeguarding their data and IT assets.
- SOLUTIONS
- RESOURCES
2025 Vulnerability Statistics Report
Discover the most common weaknesses faced by enterprises to enable data-driven decisions for managing risks and exposures more effectively.
- ABOUT US
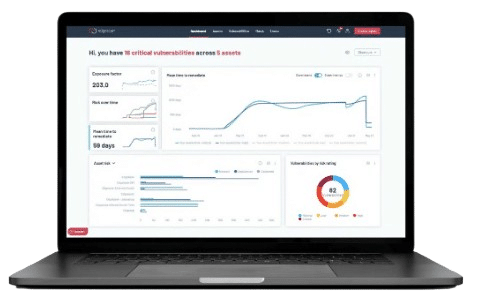
One platform to strengthen your CTEM program
Edgescan offers a continuous security testing and unified exposure management SaaS platform that manages thousands of assets for businesses large and small in a wide variety of industries across the globe.
- PARTNER
- KNOWLEDGE BASE
- THE PLATFORM
- FEATURES
The Edgescan Platform eliminates the need for tool configuration, deployment, and management.
By providing vulnerability intelligence and remediation information along with human guidance and vulnerability verification, we help our customers prevent security breaches, safeguarding their data and IT assets.
- SOLUTIONS
- RESOURCES
2025 Vulnerability Statistics Report
Discover the most common weaknesses faced by enterprises to enable data-driven decisions for managing risks and exposures more effectively.
- ABOUT US
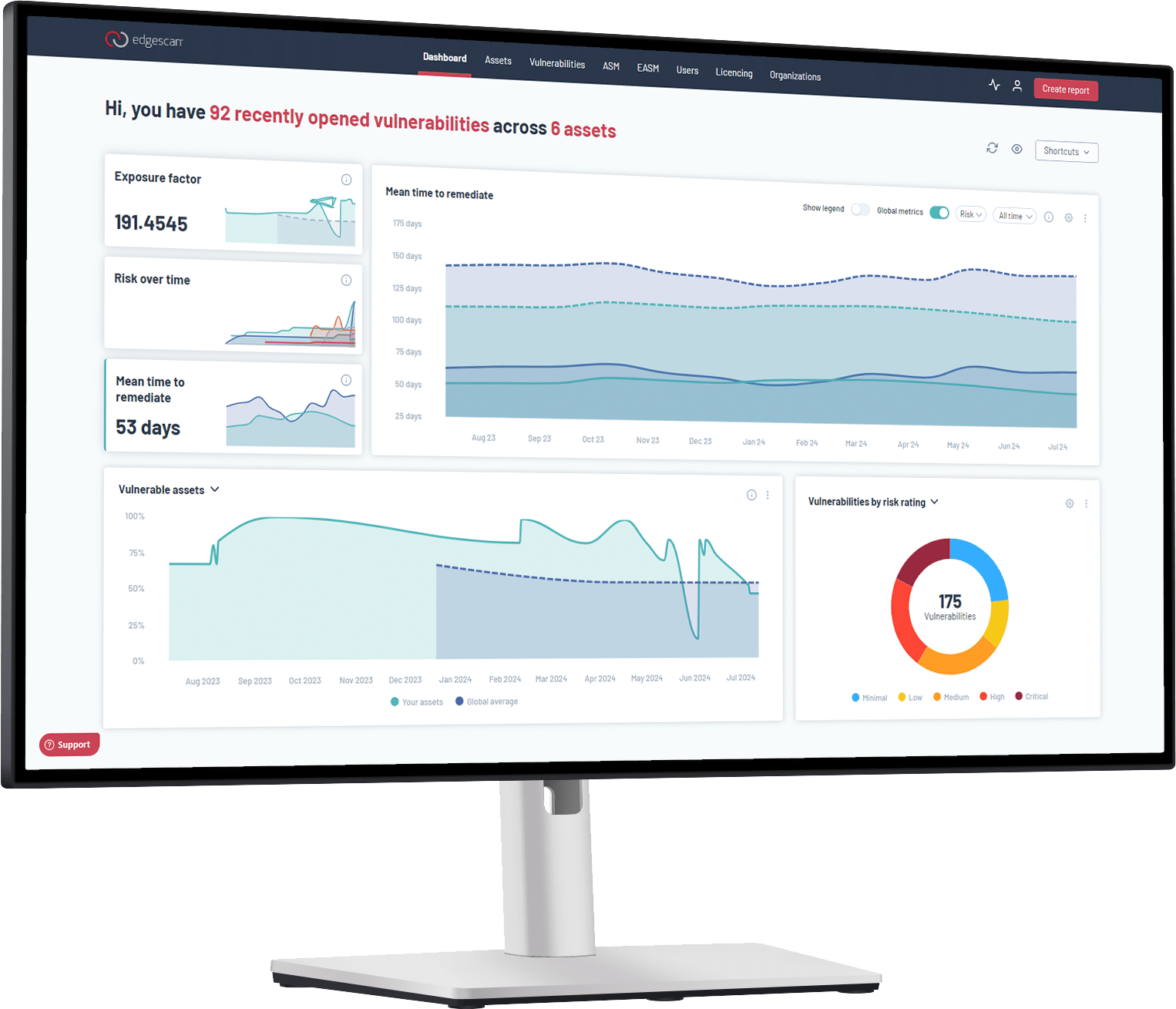
One platform to strengthen your CTEM program
Edgescan offers a continuous security testing and unified exposure management SaaS platform that manages thousands of assets for businesses large and small in a wide variety of industries across the globe.
- PARTNER
- KNOWLEDGE BASE
- THE PLATFORM
- FEATURES
The Edgescan Platform eliminates the need for tool configuration, deployment, and management.
By providing vulnerability intelligence and remediation information along with human guidance and vulnerability verification, we help our customers prevent security breaches, safeguarding their data and IT assets.
- SOLUTIONS
- RESOURCES
2025 Vulnerability Statistics Report
Discover the most common weaknesses faced by enterprises to enable data-driven decisions for managing risks and exposures more effectively.
- ABOUT US
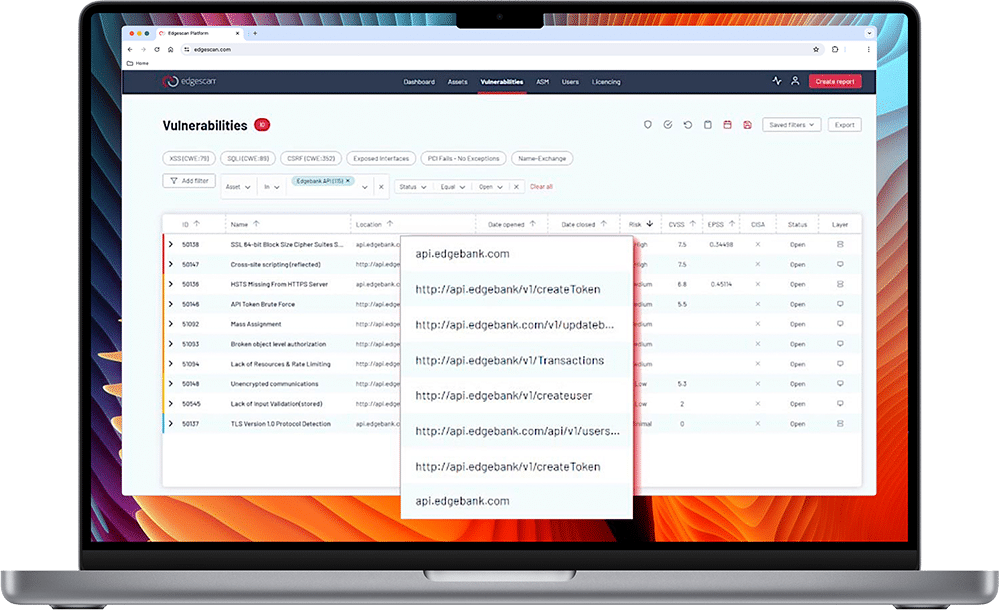
One platform to strengthen your CTEM program
Edgescan offers a continuous security testing and unified exposure management SaaS platform that manages thousands of assets for businesses large and small in a wide variety of industries across the globe.
- PARTNER
- KNOWLEDGE BASE